Building from Source
Building the Editor
Oni2 can be built from source using the following setup and steps!
This takes around 30-40 mins on an "average" machine, as we need to setup a brand new
set of tooling for both OCaml and Skia, which are both fairly large. Repeat builds
should take only a few seconds, as build artifacts are cached by esy.
Prerequisites
When performing a non-Docker based install, you'll need the following dependencies on all platforms. There are additional platform specific dependencies linked below.
- Install Git
- Install Node
- Install Esy (0.6.10 or above is required, but the latest version is recommended:
npm install -g esy@latest)
NOTE: Linux-only: if you need to install using
sudo npm install -g esy@latestthen your NPM installation might be broken follow the instruction here to fix it this is related to this issue esy/esy#1099.
- Check the Revery dependencies for your platform: https://github.com/revery-ui/revery/wiki/Building-&-Installing.
- Windows-only: Run
npm install -g windows-build-tools(this installs some build tools that aren't included by default on Windows) - Install any other system packages required by Oni2 dependencies, as outlined below.
Dependencies
All platforms require git, node and esy, and anything outlined in the revery docs:
https://github.com/revery-ui/revery/wiki/Building-&-Installing.
Windows
No additional requirements.
macOS
Requires libtool and gettext from homebrew: brew install libtool gettext.
Linux
Some Linux distributions may need other packages:
- Ubuntu :
nasm,libacl1-dev,libncurses-devlatter two forlibvim. - Fedora/CentOS :
libXt-devel,libSM-devel,libICE-devel,libacl-develandncurses-develforlibvim - Xorg related libraries:
libglu1-mesa-dev,libxxf86vm-devandlibxkbfile-dev.
Docker build (Linux)
The docker build path is the most contained path, and as such may be the easiest way on
some Linux distributions. We include a Dockerfile in scripts/docker/centos that we use
for all our CI builds, so it should be up-to-date! This will produce an AppImage and
tar.gz both suitable for Linux. Containers are not provided for other distributions
(we only need this one), but should serve as a good base if specific changes are needed.
The steps to use it are as follows:
# Clone the Oni2 repo
git clone https://github.com/onivim/oni2
cd oni2
# Use our included script to setup a docker container
docker build --network=host -t centos scripts/docker/centos
# Now use that container to actually build an Oni2 AppImage.
# Bind the Oni2 folder to the volume so that it can access the source.
# We also bind ~/.esy such that the build steps are cached locally.
# This means subsequent builds are fast.
# You can clean that folder out to save space at the cost of build time for future
# builds.
docker container run --rm \
--name centos \
--network=host \
--volume `pwd`:/oni2 \
--volume ~/.esy:/esy/store \
--cap-add SYS_ADMIN \
--device /dev/fuse \
--security-opt apparmor:unconfined \
centos \
/bin/bash -c 'cd oni2 && ./scripts/docker-build.sh'
# Wait 30-40 minutes on an average machine...
# This takes up to about an hour on CI though, so may be worth
# leaving for a bit!
# During the initial esy steps, there isn't much output, so you
# may end up waiting on `info fetching: done`. It will eventually
# finish the initial install and move on to building, which has output.
# Done!
# This should drop an AppImage binary off in _release in the Oni2
# folder.
# You can run a health check if you would like...
_release/Onivim2.AppDir/usr/bin/Oni2 -f --no-log-colors --checkhealth
Build and Run from Source
Clone repository
git clone https://github.com/onivim/oni2
cd oni2
Install node dependencies
npm install -g node-gyp
node-gyp install 14.15.4
node install-node-deps.js
NOTE: The non-standard
node install-node-deps.jsstep instead ofnpm installis necessary because the script picks up our vendored node binary.
NOTE: The
node install-node-deps.jscommand will need to be re-run whenever the extension host is upgraded.
Build the front-end
NOTE: On Windows, you must build from a shell running as administrator. This is a requirement of esy because creating symlinks requires administrator permissions. More info at esy/esy#389.
NOTE: On macOS, if you receive an
error: Too many open files, you can runulimit -Sn 4096to increase the file limit. More info at esy/esy#1057
# Install dependencies in package.json
esy install
# Builds most dependencies and run Oni2 specific bootstrapping.
# Takes upwards of 30 mins on a normal machine.
# esy does intelligently cache to ~/.esy, subsequent builds are fast.
esy bootstrap
# Finish up remaining parts of building. Should be quick.
esy build
Run health-check
The
--checkhealthargument validates all dependencies are available and working.
esy run -f --checkhealth
Run Onivim 2
esy run
Tests
esy '@test' installesy '@test' buildesy '@test' run
Inline Unit Tests
esy '@test' inline
Check build
esy build dune build @check
Benchmarks
esy '@bench' installesy '@bench' buildesy '@bench' run
Format code
We use auto formatting tool, you might want to run it before you commit changes
esy format
Release
NOTE: On macOS, checkhealth may report that a library is not loaded (e.g. Sparkle). This is normal. To check that libraries are loaded in a generated release build, see the section on macOS below.
To create a release build, run:
esy '@release' run -f --checkhealthesy '@release' installesy '@release' run --helpesy '@release' create
This will create a _esy/release folder at the root with the application bundle inside that folder there will be folders for built binaries, in _esy/release/install/bin the Oni2 binary resides along Oni2_editor.
With the exception of macOS, these are actually symbolic links to oni2/_esy/release/store/b/oni2-<hashvalue>/install/default/bin/Oni2, the same is true for the Oni2_editor binary. On macOS, the symlinks are replaced with the actual binaries.
Windows
To create an installation package for Windows, run the following PowerShell script:
./scripts/windows/publish.ps1
macOS
When building a release on newer versions of macOS, checkhealth will report that some libraries are not loaded. This is because the libraries are not accessible until the app is fully built and can be ignored.
To check that the libraries are in fact included in a generated release build, you can run the following command from the oni2 directory:
./_release/Onivim2.app/Contents/MacOS/Oni2 -f --checkhealth
You can also install Oni2 in your Applications folder.
Run the following from the oni2 directory:
cp -R _release/Onivim2.app /Applications
If you want to open the editor from the terminal with an oni2 command, you can add Oni2 to the system PATH using a command
from within the app:
- Open Oni2 from launchpad
- Open command palette with
Cmd + Shift + P - Execute:
System: Add Oni2 to System PATH
Extension Integration
If you want to develop, or debug, an extension integration, the following tips may help:
Testing with oni-dev-extenion
There is a development extension in src/development_extensions/oni-dev-extension which can be used to implement dummy functionality that is often easier to test and integrate with than real extensions.
Resources
Instrumenting extensions
To add logging, use console.error - messages on stderr will be shown in Onivim's log. (Make sure to turn debug logging on, via ONI2_DEBUG=1 environment variable or the --debug command-line arg).
Both the oni-dev-extension and any other extension can be instrumented, as they're usually included in non-minified form.
Extension host
If there's a problem in-between Oni2 and the extension, it can be helpful to build and instrument your own copy of the extension host.
Building
- Navigate to your home directory (ie,
cd ~on Linux / macOS, orcd /on Windows) git clone https://github.com/onivim/vscode-exthostcd vscode-exthostyarn installyarn compile
You can use the yarn watch command too - this is useful for iterating quickly!
Testing
You can use the ONI2_EXTHOST environment variable to override the default extension host with your local extension host:
- `ONI2_EXTHOST=/Users/<your-username>/vscode-exthost esy run -f --debug``
For example, adding the logging here (the $executeContributedCommand proxy method)
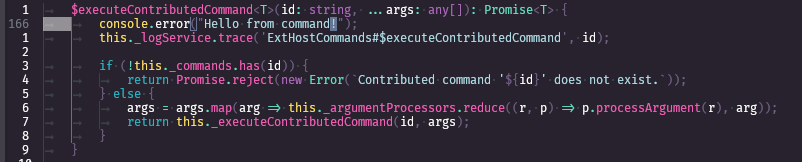
Results in this debug logging:

Protocol
The extension host protocol is defined in extHost.protocol.ts. Interfaces prefixed with MainThread refer to messages sent from the extension host to the "main thread", which in our case is Oni2. While interfaces prefixed with ExtHost refer to messages sent to the extension host.
Building the Documentation Website
From the oni2 directory:
cd docs/websitenpm installnpm start
